Aphids
Aphids (superfamily Aphidoidea) are known to transmit over 150 different kinds of plant viruses, including beet mosaic, cabbage black ringspot, carnation latent, cauliflower mosaic, cherry ringspot, cucumber mosaic, onion yellow dwarf, pea wilt, potato Y, tobacco etch, tobacco mosaic, tomato spotted wilt, and turnip yellow mosaic.

Leafhoppers
Leafhoppers (family Cicadellidae) transmit over 80 known types of plant disease, including ones caused by viruses, mycoplasma-like organisms (MLOs), and spiroplasmas. Examples include aster yellows, beet curly top, blueberry stunt, dwarf disease of rice, phony peach, and Pierce’s disease of grapes.

Planthoppers
Planthoppers (superfamily Fulgoroidea) have been implicated as vectors in the transmission of about 20 plant diseases (viruses and MLOs) including cereal tillering disease, maize mosaic, Northern cereal mosaic, oat sterile dwarf, rice hoja blanca, rice stripe, and sugarcane Fiji disease.

Whiteflies
Whiteflies (family Aleyrodidae) are responsible for transmitting yellow mosaic diseases in at least 20 plant species including cowpeas, roses, soybeans, and tomatoes. Whiteflies also spread leaf curl viruses in cotton, potato, tomato, tobacco, and other plants.

Treehoppers
Treehoppers (family Membracidae), especially Micrutalis malleifera, transmit a viral pathogen that causes pseudo-curly top disease in eggplants and other Solanaceae.

LINKS
Mealybugs
Mealybugs (family Pseudococcidae) are known vectors of several plant viruses including cocoa swollen shoot virus and cocoa mottle leaf virus.

LINKS
Psyllids
Psyllids (family Psyllidae) are the vectors of mycoplasma-like organisms responsible for pear decline and greening disease of citrus.

LINKS
Ash-gray leaf bugs
Ash-gray leaf bugs (family Piesmatidae) are vectors of the beet leafcurl virus, the sugarbeet savoy virus, and beet latent rosette disease.

LINKS
[/tab]
Flower thrips
Flower thrips (family Thripidae) are suspected of transmitting bacterial, fungal, and viral pathogens. Tomato spotted wilt virus, for example, is spread by onion thrips (Thrips tabaci) and tobacco thrips (Frankliniella fusca).

[/tab]
Apple maggot
Apple maggots, Rhagoletis pomonella (family Tephritidae), are vectors of Pseudomonas melophthora, the pathogen of bacterial rot in apples.

LINKS
Cabbage maggots
Cabbage maggots, Delia radicum (family Anthomyiidae) spread the fungal pathogen of blackleg (Phoma lingam).

Leafminer flies
Leafminer flies (family Agromyzidae) in the genus Liriomyza are capable of transmitting tobacco mosaic virus and sowbane mosaic virus.

LINKS
Leaf beetles
Leaf beetles (family Chrysomelidae) spread more than 35 plant viruses including broad bean mottle, turnip yellow mosaic, southern bean mosaic, and rice yellow mottle. Potato flea beetles (Epitrix cucumeris) spread the pathogen of potato scab (Actinomyces scabies) when the larvae enters a tuber. Corn flea beetles (Chaetocnema pulicaria) and corn rootworms (Diabrotica spp.) are responsible for spread of Bacterium stewarti, the bacterial pathogen of Stewart’s disease in corn.
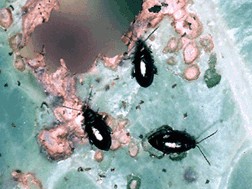
Bark beetles
Bark beetles (family Scolytidae) are vectors of fungal pathogens in trees. The elm bark beetle (Scolytus multistriatus) infects elms with Ceratocystis ulmi, the pathogen of Dutch elm disease. A similar blue stain fungus (Ceratocystis ips) is spread among pine trees by the pine engraver (Ips pini) and other bark beetles. The pathogen for chestnut blight (Endothia parasitica) is also spread by the Scolytidae.

Plum curculio
Plum curculios, Conotrachelus nenuphar (family Curculionidae), inoculate fruits of peach cherry and plum with Sclerotinia fructicola, the fungal pathogen of brown rot.

Honey bees
Honey bees, Apis mellifera (family Apidae), and other pollinating insects spread the bacterial pathogen of fire blight (Erwinia amylovora) as they travel from tree to tree collecting nectar.

Ants
Ants (family Formicidae) and bees spread the pathogen for mummy berry, a blueberry fungus, from stem lesions to fruit as they forage for food.


